Diagnosis of glandular fever
introduction
The diagnosis of glandular fever is mainly made clinically and then confirmed by laboratory tests. Correct diagnosis is particularly important because differential diagnosis therapies are different and sometimes contraindicated.
You should also be able to take the right steps early to relieve symptoms and avoid complications. Even today, the safe diagnostic procedures only deliver reliable results after a few days. A good description of the symptoms is important for the attending physician.
General information can be found here: Pfeiffer's glandular fever

This is how it can be diagnosed
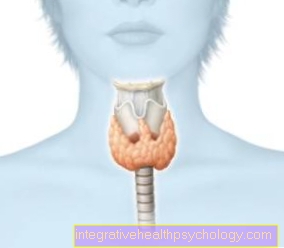
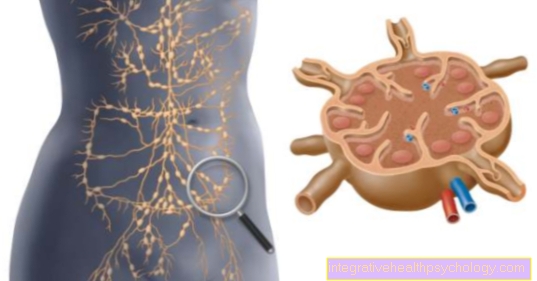
The basis for the diagnosis of glandular fever is the detailed description of the disease history by the patient and a detailed physical examination. Important aspects are the inspection of the throat, palpation of the lymph nodes all over the body and the examination of the spleen and liver, sometimes through an assessment using ultrasound. There it can quickly be measured whether the spleen and liver are enlarged, as can occur in infectious mononucleosis. In the pharynx, there is a classic bilateral enlargement of the pharynx with grayish-white coatings.
You might also be interested in: You can recognize Pfeiffer's glandular fever by these symptoms
Then blood is drawn from the patient and examined in the laboratory for various parameters. A so-called blood smear is made from the blood, which makes it possible to assess the individual blood cells under the microscope. There you can see Pfeiffer cells and an increase in lymphocytes. It is then important to examine the blood serum carefully for certain antibodies that the human immune system generates and activates when the Epstein Barr virus attacks the organism. All these parameters are brought together and a well-founded diagnosis can then be made.
Read more about this at: Blood values in Pfeiffer's glandular fever - these parameters are important
examination
The clinical physical examination is the most important factor in diagnosing Pfeiffer's glandular fever. Due to possible differences in the occurrence of symptoms, many years of clinical experience is necessary in some cases in order to choose the correct one from among the potential differential diagnoses. The Inspection of the throat, palpation of lymph nodes all over the body, temperature measurement, inspection of the eardrums, examination of the skin for possible rashes, and palpation of the liver and spleen are mandatory.In severe clinical cases, involvement of the heart, kidneys, brain and joints should be ruled out at an early stage.
Laboratory values in Pfeiffer's glandular fever
There are some laboratory values that can indicate an infection with the Epstein Barr virus even before the antibody test is received. For example the LDH, the Lactate dehydrogenase, is an unspecific indicator of cell death and is significantly increased in Pfeiffer's glandular fever.
It is also important to examine the liver values (AST and ALT), as these can be increased in EBV. In addition, an increase in lymphocytes can be shown in the blood count. In addition, the laboratory values can possibly rule out other diseases.
smear
In the course of the clinical diagnosis, a smear of the tonsils can also be taken. A classic symptom of Pfeiffer's glandular fever is Tonsillitis with greyish-white coatings. By swabbing these deposits with a cotton swab, laboratory diagnostics can then determine whether the tonsillitis was caused by bacteria. If this is the case, antibiotics must be used.
However, this smear is not sufficient for a diagnosis of Epstein Barr Virus, as the information is not clear enough. So the smear serves much more to exclude differential diagnoses.
ELISA method
By an ELISA test (Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay), a method of protein analysis, the interaction between antibodies and antigens can be observed. IgM antibodies, which in this case are VCA-IgM antibodies against the viral capsid antigen, are used to detect an acute infection. They are acutely elevated and return to normal after a few weeks. VCA-IgG antibodies only become positive after a few weeks, but remain detectable in the blood for a lifetime. Antibodies against the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen Anti-EBNA-1 (IgG) indicate that the infection has healed. And early antigen anti-EA IgGs are a marker for an incipient disease even before the IgM antibodies rise.
That is how long it takes to make a diagnosis
For the correct diagnosis, the clinical symptoms are first of all decisive. The pathologies that the body obviously shows - for example in the throat, lymph nodes or through the enlargement of the spleen directly can be determined by the first examination by the doctor.
The blood tests for liver values and the blood count get depending on the laboratory some hours or at the latest the next day the results.
The results of the antibody test are usually only obtained after a few days to weeks.
Is there a rapid test for glandular fever?
There is also a rapid test procedure for infection with the Epstein Barr Virus. This can be based on Reactions to sheep erythrocytes or by one Latex agglutination test respectively.
Unfortunately, the results of these examinations are not reliable and often show false positive or false negative results. However, this depends on the age of the patient, the execution of the test and the stage of the disease. The results are often falsified by infections with other pathogens.
Recommendations from our editorial team
- Treatment of Pfeiffer's glandular fever
- Glandular fever in the child
- Glandular fever in babies
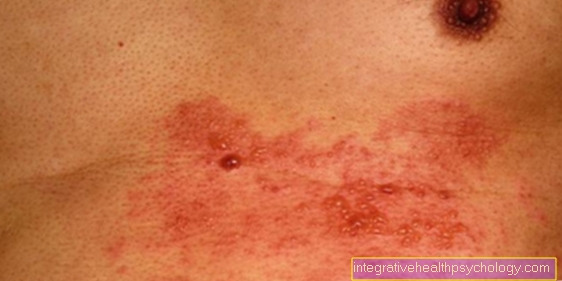
- Rash in Pfeiffer's glandular fever
- Duration of Pfeiffer's glandular fever
- Blood values in Pfeiffer's glandular fever - these parameters are important