The operation of a bursitis
synonym
medical: Bursitis
definition
There are bursae on many parts of the body. They serve to "cushion" protruding bones, inflammation occurs primarily in the context of injuries or mechanical overstress.

therapy
Depending on how they develop, bursitis is initially treated conservatively and rarely surgically.
Aseptic inflammations, i.e. those in which no bacteria have penetrated and complicate the inflammation, are usually conservative by means of cooling, protection and anti-inflammatory medication (Anti-inflammatory drugs) treated.
If this does not improve, this is usually an indication for surgical therapy.
Read more on the subject at: Duration of bursitis
Septic bursitis, i.e. those in which there is an additional infection, must also be tackled surgically in some cases, as there is a risk of the infectious agents spreading in the body, which in the worst case can lead to sepsis.
Septic inflammation usually occurs as part of injuries, as the destruction of the skin barrier enables the bacteria to penetrate deeper into the tissue. Nowadays, however, even with septic bursitis, non-surgical treatment using antibiotics is increasingly sought.
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- Lumedis - orthopedic surgeons
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see Lumedis - Orthopedists.
Action

The goal of the operation is usually one complete removal of the bursa, the so-called Bursectomy.
The disadvantage of this variant is that the operation has to be open, which means that a sufficiently large skin incision has to be made, which on the one hand leads to scarring and on the other in the area of one Joint - albeit rarely - can lead to functional restrictions.
Another variant of the operation is that Bursoscopy, in which instruments are introduced into the bursa by means of very small incisions in the skin under vision, with the aid of which the inflamed inner lining (synovial mucosa) of the bursa is carefully removed.
This procedure is particular in chronic inflammatory processes used, it still finds essential less common Use as the bursectomy.
Risks
During an operation on a bursa, there are typical operational risks such as the risk of bleeding and nerve lesions and thus (mostly temporary) limitations in sensitivity in the surgical area. As with any operation, there is also a risk of infection from pathogens that can penetrate the wound during the operation.
forecast
Surgical removal of the bursa usually results in a complete resolution of symptoms.
Operation on the knee
Inflammation of the bursa in front of the kneecap (Prepatellar bursitis) is caused by chronic pressure overload or blunt trauma.
If there is an open injury to the bursa, an infection with bacteria can also occur.
Surgical treatment of knee bursitis offers two options.
On the one hand, the bursa can be partially removed.
A bursoscopy (Bursoscopy) only the inner part of the bursa is removed, while the outer sliding layer is retained.
This method is less risky and the wound healing process is faster. However, this surgical technique is not always possible or effective.
On the other hand, the inflamed bursa on the knee can also be completely removed.
This operation is usually performed under general anesthesia and the person concerned lies on their back so that the surgeon can see the knee clearly.
A cuff is placed above the knee, called a tourniquet, which reduces bleeding during the operation.
The bursa is completely removed and a widespread wound remains in the knee area, which heals with scarring.
A drain is often placed in the wound for some time so that blood and wound secretions can drain away.
In some cases, the wound on the knee is not completely closed immediately, but only in a second step.
This can be particularly necessary in the case of infectious bursitis.
After the operation, the leg must be spared, usually aids such as splints or a cast are put on.
Physiotherapy and the use of pain reliever medication follow the operation.
Read our article on this: Duration of bursitis on the knee
Operation on the shoulder
A Bursitis in the shoulder is usually started with conservative methods treated.
Only when these therapies are insufficient and the symptoms persist in the shoulder can a surgical removal of the bursa should be indicated.
This is part of a Shoulder arthroscopy (Arthroscopy) with the help of "Keyhole method"the bursa is removed in a minimally invasive manner.
As part of this intervention, a Expansion of the so-called subacromial space carried out.
A part of the shoulder roof is milled off in order to create a little more space in the inflamed shoulder and to avoid a recurrence of bursitis.
In the Arthroscopy of the shoulder the surgeon will also assess the condition of the tendon attachments Shoulder muscles (Rotator cuff). If necessary, a required Reconstruction of this vision (e.g. with a crack) in the same procedure.
Operation on the elbow

The acute Bursitis on the elbow (Olecranon bursitis) is often caused by trauma (e.g. Bruise, fall) caused.
But also metabolic diseases like that gout, chronic irritation of the elbow (e.g. by propping up to read) or Rheumatoid arthritis can cause inflammation of the elbow bursa.
The acute olecranon bursitis can be treated well by making an operative incision (surgical incision in the tissue) and allows the purulent secretion to drain away.
It may be useful to empty the bursa completely and then with it Glucocorticoids (cortisone) should be filled to prevent re-ignition.
A chronic inflammation of the bursae the elbow often has to be treated surgically. This is where the bursa becomes completely removed and the elbow using a Upper arm splint immobilized until the surgical wound has healed (about five to seven days).
Thereafter, further treatment with elastic bandages respectively.
In case of a septic olecranon bursitis (bursa infected with bacteria), the wound may need special treatment.
Here you can Antibiotic chains placed in the wound for a few days.
Often this leads to permanent success and the bursa forms again.
Basically, bursitis on the elbow must be operated on if it purulent or chronic or when the nonsurgical therapies have failed.
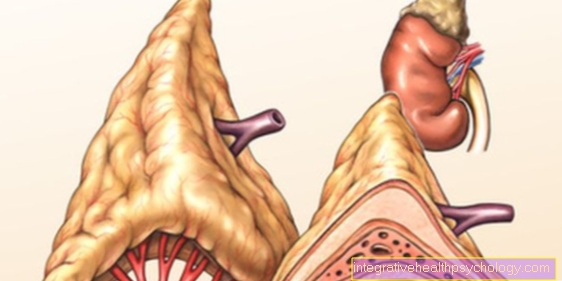
Figure bursitis on the elbow
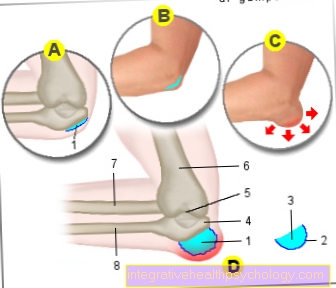
- Bursa
of the elbow -
Bursa subcutanea olecrani - Connective tissue layer -
Stratum fibrosum - Synovial layer -
Synovial stratum - elbow
(Approach of the arm extensor) -
Olecranon - Upper arm-ulnar joint -
Articulatio humeroulnaris - Upper arm shaft -
Corpus humeri - Spoke shaft -
Corpus radii - Ellschaft -
Corpus ulnae
A - bursa of the elbow
(Light blue) - normal
B - elbow - normal
C - bursitis
at the elbow - Olecranon bursitis
D. - Anatomy of the inflammation of a
Bursa on the elbow
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Heel surgery
A Bursitis on the heel (Subachillic bursitis) is mostly pronounced by the standard variant of a Heel hump (Haglund pseudoexostosis) or by external pressure (e.g. from poor footwear) caused.
Of the permanent irritation leads to inflammation of the bursa and often causes severe pain.
The surgical treatment of this bursitis therefore usually does not only include that complete removal of the bursa on the heel but also requires that Removal of the heel humpon which the Achilles tendon starts.
Immediately after the operation, it is advisable to take care of the heel and keep it calm. Often a Lower leg respectively Foot rail created.
About four days after the operation, the foot can be fully loaded again and a functional treatment in the so-called Stable shoe Start with a one to two centimeter heel elevation.
This should be for about four weeks and the heel rise is then gradually reduced again.
It usually passes before running loads are possible again eight to twelve weeks.
Especially if there is an intervention on the Achilles tendon was required should the athletic load after twelve weeks at the earliest start with physiotherapy should of course be started earlier.
Operation on the hip / thigh
In the case of bursitis on the hip or thigh, the operation is an alternative treatment method if conservative therapy with, for example, medication and cooling has not been successful.
The aim of the operation is to prevent the tissue-damaging process and the associated pain of bursitis and to enable pain-free movement of the hips and thighs again.
Bursitis can have various causes, which is an important factor in the decision for or against an operation.
If the bursitis of the hip is caused by a bacterial infection or an underlying rheumatic disease, surgery should be avoided as it would increase the risk of postoperative complications.
If the bursa is overloaded by too much or incorrectly performed movement, surgical treatment will achieve a good result. There are two different ways to operate on bursitis.
The entire bursa can either be removed through an open access so that there can be no new process. Or with a kind of bursa mirroring, the innermost layer of the bursa is removed by making small cuts so that the remaining residue can simply heal again. Both procedures have their advantages and disadvantages, which certainly has something to do with the scars that occurred after the operation.
However, antibiotic and antithrombotic prophylaxis should always be given.
Duration of the operation

Depends on the Location and size of the bursa as well as from Degree of inflammation present the length of time it takes for the wound to heal after an operation and for full functionality to be restored can vary.
As a rule, surgery in the area of a bursa cannot be performed on an outpatient basis.
Outpatient treatment is only possible with one Puncture of the bursa, but not possible with a complete or partial removal.
Will the bursa under a Jointoscopy removed or partially removed, usually only a short inpatient stay is necessary.
The Wound healing happens quickly and the rehabilitation of the affected joint physiotherapy exercises can be done early.
However, if the bursa is surgically removed, a longer hospital stay and extended follow-up treatment over a few weeks must be expected.
Immediately after the operation, a Articulated splint laid out under the one elastic bandage is wrapped. This achieves a compression effect that prevents fluid accumulation in the wound, swelling or bleeding.
Depending on how extensive the wound cavity is, such a dressing should be used for two to three weeks be worn.
Immobilization after the operation is generally not necessary.
The sutures with which the wound is closed can after 12 to 14 days removed.
Movement exercises can be started on the first day after the operation.
However, the affected joint should be used for four to six weeks after surgery, for example, should be done after surgery on the shoulder no heavy weights lifted and Activities above shoulder height are avoided.
Because of this, there is usually an occupational downtime of two to four weeks to be expected. However, this depends on the findings of the bursa and the requirements and stresses at the workplace.
Read more on the subject below Surgery for bursitis on the elbow.


.jpg)