Elbow osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis of the elbow joint
Under the term arthrosis one grasps the Group of chronic degenerative diseases together. These are characterized by the Articular cartilage is worn out what is part of the natural wear and tear during the aging process and on the other hand by certain Dream can happen.
Through these changes in the cartilage, the bone affected, causing it to Pain, Swelling, Tension and in the worst case too Restrictions on movement and Deformations in the joint can come. Such osteoarthritis can in principle in everyone joint of the human body, but it is most commonly found in hip joint or Knee joint.

Osteoarthritis in Elbow (Elbow osteoarthritis) is mostly the Result of an accident, for example a broken elbow. Also existing over a longer period of time heavy loads of Elbow joint also favor elbow osteoarthritis. Also can Misalignments of the bones within the elbow joint (for example Cubitus varus and Cubitus valgus) contribute to the development of osteoarthritis.
In general, men are affected somewhat more often and age is also a risk factor, as the signs of wear and tear are more pronounced here than in younger people.
Elbow osteoarthritis is usually noticeable first through pain. These initially only exist now and then for a few days and then completely disappear for a certain time. In the course of time, however, the pain-free episodes become increasingly rare and shorter, the pain becomes stronger and sometimes begins right down to the forearm and / or the shoulder to broadcast.
While these complaints initially almost exclusively when moving occur at some point even at rest noticeable.
Characteristically for a Elbow osteoarthritis there is also one Stiffness of the joints, the especially in the morning clearly emerges. The mobility of the elbow joint can be restricted if, in the course of advanced osteoarthritis, small pieces of bone or cartilage detach and are free in the joint.
The restriction of movement is also favored by the often existing swelling of the elbow. In many patients, movement in the joint is also involved classic crunching sound perceive.
The diagnosis an elbow osteoarthritis can in the vast majority of cases roentgen can be made relatively safe, as very typical changes can be shown in the X-ray images.
Appointment with an elbow expert?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
As a former performance-oriented tennis player, I specialized early on in the conservative treatment of the elbow.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
The appropriate therapy an elbow osteoarthritis always consists of two pillars.
For one thing, they should Pain treated with medication become.
Are particularly effective in this clinical picture Painkillers from the antirheumatic type (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: NSAIDs), such as Ibuprofen or Diclofenac. These not only relieve the pain, but also counteract any inflammatory reaction in the joint.
Complementary are with osteoarthritis physiotherapy measures really important. It is important for the patient to find a good balance by moving and loading the joint not excessively but still sufficiently. Therefore, at least initially, exercises should always be carried out under the supervision of a doctor or physiotherapist. It is advisable to use the Musculature to train the forearm with special exercises to stabilize the joint and support it in its movements. Aids such as straps, grip devices or therapy balls can be used for this purpose.
In the event of an acute episode, it can also be useful to cool the sore joint. Surgical intervention should only be carried out if none of these measures show any improvement in the symptoms even after a long period of time and the elbow joint has still not regained its full mobility or if there are very pronounced deformities.
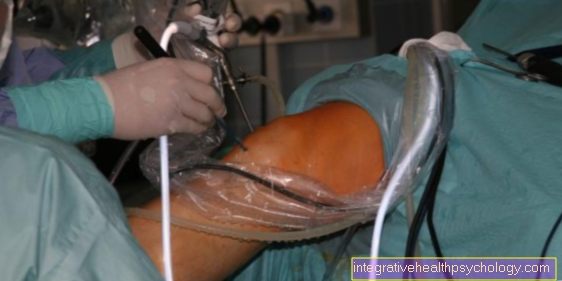
A surgery can open or by Arthroscopy respectively.
Depending on the findings, the cartilage surface is smoothed, the joint surfaces are cleaned, loose fragments of cartilage or bone tissue are removed and / or adhesions are loosened. In extreme cases, as with any other joint, the elbow joint can be removed and replaced with a prosthesis.
Due to the various treatment options for elbow osteoarthritis, almost all patients can have considerable reduction in complaints and often even one Freedom from symptoms can be achieved.
Symptoms
The symptoms of elbow arthrosis, that is, the progressive damage to the articular cartilage in the elbow joint, are varied and sometimes also present in other diseases.
However, pain is almost always present, which is particularly noticeable during exercise and exertion and can also occur at rest and at night as the disease progresses.
These can also radiate into the shoulder and forearm. In addition, the pain intensity increases and the duration of the phases in which you do not feel pain becomes shorter. As an additional symptom one can partially with the elbow osteoarthritis cracking or rubbing noises, Called crepitations, hear and feel them.
Due to the constant irritation caused by the elbow osteoarthritis in the joint the surrounding tissue swells, the elbow becomes thick. A typical symptom of elbow osteoarthritis is the phenomenon that one has initial difficulties in moving the arm fully in the morning or after longer breaks. Other symptoms include muscle tension. Some people notice a slight worsening of symptoms in cold or wet weather.
Overall, the elbow arthrosis can restrict the freedom of movement of the joint. Patients can no longer fully extend or bend their arm. How much the mobility decreases due to pain, swelling and other symptoms varies from case to case and depends on the degree of elbow arthrosis. In severe cases, the joint can stiffen completely, favored by small detached fragments of cartilage or bone.
therapy
In the treatment of elbow osteoarthritis, one must differentiate between conservative therapy concepts and surgical approaches.
Conservative therapy aims to improve symptoms without surgery and thus make the joint more flexible and painless or painless. The advantage of this therapy is that you do not need any intervention and the associated risks are avoided. This procedure is recommended for mild to moderately advanced elbow osteoarthritis.
The first pillar of conservative therapy is drug treatment with drugs from the group of so-called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (best known example: aspirin).
These are substances that on the one hand have a good pain-relieving effect and on the other hand counteract inflammatory processes in the joint. Preparations to be mentioned that are used in elbow arthrosis are Ibuprofen or Diclofenacwhich are used in many orthopedic diseases. There is also the possibility of small amounts Cortisone, an anti-inflammatory drug, injected directly into the joint.
In addition to medication, the most important measure in conservative therapy for elbow osteoarthritis is extensive physiotherapy. Various exercises are performed under professional guidance that are intended to make the elbow joint more flexible or to keep it flexible (movement therapy). It works with ribbons, balls, but also under water.
In addition, targeted treatments with cold or heat can be used. In some cases, however, it is also advisable to immobilize the joint for a short time with certain splints (orthotics), especially if a severe inflammation is underway.
An operation of the elbow joint is useful if the above measures are insufficient and show no improvement or if the elbow osteoarthritis is very advanced. Then one can either openly or arthroscopically, i.e. Under camera view and through a very small incision, free the joint cavity of free fragments and smooth cartilage and bones.
Finally, there is the possibility of artificially replacing the entire joint by inserting a full elbow prosthesis. In General or partial anesthesia a titanium artificial joint built into the humerus and forearm bones with special cement, whereby most of the bones are retained.
As a rule, this procedure takes about 1-2 hours and the hospital stay is on average one, a maximum of two weeks. It is important to have a targeted one after this operation physical therapy, with which you can cope with most everyday things again after about 6 weeks. However, heavy loads are no longer possible after this.
Figure elbow joint

- Upper arm head -
Capitulum humeri - Outer femoral knot -
Lateral epycondilus - Inner femoral knot -
Epycondilus medialis - Upper arm roll - Trochlea humeri
- Upper arm shaft -
Corpus humeri - Spoke head - Caput radii
- Spoke neck - Collum radii
- Roughness of the spoke -
Radial tuberosity - Roughness of cubit -
Ulna tuberosity - Spoke shaft -
Corpus radii - Ellschaft -
Corpus ulnae - Articular cartilage
- Joint capsule -
Articular capsule - Ellen's nerve -
Ulnar nerve - Arm extensor -
Triceps brachii muscle - Upper arm muscle -
Biceps brachii muscle
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations













.jpg)