Mallory-Weiss Syndrome
overview
Mallory-Weiss syndrome is a disease of the esophagus (Esophagus) or the stomach. Frequent gagging and vomiting lead to tears in the esophageal mucosa, usually when the mucosa has already been damaged. A common reason for a damaged mucous membrane is excessive alcohol consumption.
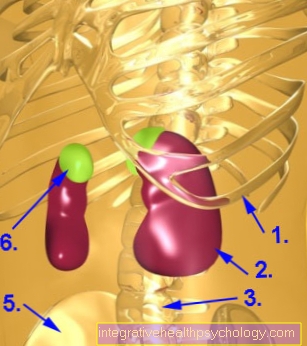
In Mallory-Weiss syndrome, bleeding occurs from the torn gastric mucosa. These can be more or less strong, depending on the type of vessel. Most of the bleeding comes from veins, but if arteries are the source, it can be immediate supply to be necessary. As a rule, surgery is not necessary and the bleeding will stop on its own. The patient then vomits blood (Hematemesis).
Another prominent symptom is very strong Upper abdominal pain which may radiate into the chest. At the Boerhaave syndrome the disease process is comparable to Mallory-Weiss syndrome, but the esophagus tears. The internal wound doesn't just have to immediately treated surgically The patient must also be subjected to antibiotic therapy, otherwise the risk of a Blood poisoning (sepsis) consists. In Boerhaave's syndrome, what is known as a disease occurs behind the breastbone Annihilation pain. This is so called because the affected patients rate the pain as greatest possible.
If a high-risk pre-existing condition is known, acute epigastric pain can be a Gastroscopy to clarify the cause. In this way, hemostatic treatment is also possible if the bleeding does not stop spontaneously, as in 90% of cases. Clamps or some kind of glue are used for this. Under medical supervision, the prognosis is good. It is advisable to protect the esophagus in the future and to administer a gastric tablet.
causes
The Mallory-Weiss syndrome is caused by constantly repeated gagging or Vomit triggered. The holding apparatus of the organs cannot withstand this constant load and eventually gives way. The stomach shifts and the wall tears. Especially alcoholism is characterized by frequent vomiting due to acute intoxication, which is why the syndrome occurs particularly often in alcoholic patients. The mucous membrane in the transition from the esophagus to the stomach is made through constant contact with Gastric juice irritated and at some point damaged.
This also happens with a Reflux esophagitis. That's a mostly chronic disease in which there is increased reflux of gastric juice. Clinically this mostly shows up as heartburn. Normal Gastrointestinal infections with nausea and Vomit are connected, so to speak never Mallory-Weiss syndrome because the disease does not last long enough. If a chronic condition develops, for example one that lasts for a long time Inflammation of the stomach liningassociated with vomiting, the disease process can begin.
Also the nutritional disorder bulimia can lead to a corresponding clinical picture. In bulimia there are '' eating attacks ", in connection with which the patient vomits for one Weight gain to prevent. In addition to the physical illness value, such a disorder also has psychiatric components that often require inpatient treatment.
bulimia
Bulimia, also known as vomiting and eating addiction, is a nutritional disorder that can occur as a consequence of Mallory-Weiss syndrome. The clinical picture is characterized by repeated binge eating, in which foods of various kinds are eaten very hastily and excessively. As a result, feelings of guilt and fear of gaining weight arise. This causes the patient, mostly young women, to induce vomiting mechanically. This can lead to injuries in the throat and mouth or damage to the skin on the hands, if these are used as aids.
Later on, patients learn to vomit on command and no longer need mechanical stimuli. Frequent vomiting and the constant stress on the mucous membrane and teeth with gastric acid cause various consequences of the disease such as tooth decay or the Mallory-Weiss syndrome. Inpatient treatment is generally recommended, as not only the physical complications but also the underlying mental illness must be treated. Eating disorders are a group of serious psychiatric illnesses which, due to the resulting emotional state, can lead to suicide in case of hardship.
Accompanying symptoms in Mallory-Weiss syndrome
The tears in the mucous membrane can lead to bleeding into the stomach cavity and this in turn can trigger vomiting. The vomit is darkly colored by the combination of stomach acid and blood, "like coffee grounds". If this happens more often, the person affected experiences severe pain in the upper abdomen and loss of appetite occurs. The stomach acid can severely damage the lining of the esophagus. Continuous contact of gastric acid with the unprotected mucous membrane of the esophagus can lead to chronic inflammatory processes and consequently to esophageal cancer.
Since Mallory-Weiss syndrome is by definition restricted to the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach, there is usually no massive blood loss with shock-like conditions. This occurs when larger, deeper vessels are involved. If the blood is drained naturally via the gastrointestinal tract and reaches a volume of over 100ml / day, so-called tar stools can occur. Tar stools are caused by the bacterial breakdown of blood in the intestinal tract. The stool will turn black and sticky.
Read more about this under: Gastrointestinal bleeding or Blood in the stool - these are the causes!
nutrition
When eating after and during Mallory-Weiss syndrome, care should be taken to eat foods that are gentle on the gastrointestinal tract. It is particularly important to abstain from alcohol so that there are no repeated states of intoxication with subsequent vomiting. In addition, alcohol promotes the production of stomach acid, which irritates the sore lining. Furthermore, juices or acidic drinks such as cola should not be consumed. On the one hand, this can lead to pain when the fluids come into contact with the tears in the mucous membrane, on the other hand, healing can be delayed. The patient should also avoid foods that are difficult to digest, as these stimulate gastric acid production.
Corresponding foods include meat, fried or particularly fatty foods, and high-sugar snacks. During the healing period, such food should only be consumed to a small extent; it is even better to do without it completely. A healthy diet with vegetables and fruit, on the other hand, is easy to digest. The patient should also ensure that the food pieces are chewed thoroughly so that pieces that are too large are not swallowed.
If you have bulimia, you must pay particular attention to the phases after eating. If the patient is under professional care, supervision may be necessary so that no vomiting occurs.
Duration of Mallory-Weiss Syndrome
Most of the time, minor bleeding stops spontaneously through the coagulation system. If this is not the case, the mucous membrane and blood vessels must be treated surgically. If pressure is repeatedly exerted on the damaged mucous membrane, e.g. if vomiting continues, it will continue to bleed until the cause is corrected.
Mallory-Weiss syndrome prognosis
The prognosis depends on the severity and extent of the damaged mucous membrane and the elimination of the underlying causes. If vomiting, coughing or other causes increase the pressure in the chest, new bleeding and damage to the mucous membrane can occur again and again. It is important to eliminate the causes of chronic alcohol abuse, reflux diseases and vomiting, so that the mucous membrane can regenerate and is not further damaged.
Frequent contact of the esophageal mucous membrane with rising stomach acid can lead to tissue changes in the esophagus that are so severe that cancer precursors arise. Particularly caused by reflux diseases and persistent vomiting. The syndrome can only be cured if the triggering causes are completely eliminated and if further bleeding is treated endoscopically.
Complication of Boerhaave syndrome
In Boerhaave's syndrome, all layers of the wall of the esophagus tear (esophageal rupture). This allows food, blood, air, saliva and stomach acid to get into the surrounding tissue of the lungs. People feel severe pain behind the breastbone and their body temperature may rise (fever). In the subcutis (Subcutis) the air escaping from the esophagus can collect and form a so-called skin emphysema, which is expressed as a crackling when you stroke it. Since microorganisms can also penetrate through the tear into the middle membrane, this can lead to an inflammatory reaction and later, if it spreads into the blood, to blood poisoning (sepsis), which can spread to the lung membrane and / or the pericardium.
Read more about this under: Boerhaave syndrome and nasogastric tube
Mallory Weiss Syndrome in Children
Mallory-Weiss syndrome is rarely seen in children. Since the development and manifestation of the disease is often a long-lasting process, patients are more likely to be aged 20 to 40 years affected. The risk factor alcohol tends to be absent in children, whereby the drinking habits of some adolescents can lead to such damage in extreme cases. The eating disorder is an important aspect bulimia represent that like anorexia (Anorexia nervosa) mainly develops in adolescence. The pressure that children sometimes exert on one another, but also the change in physical characteristics, as well as the hormones during puberty, can trigger emotional crises that end in such a mental illness.