birthmark
Synonyms in a broader sense
- Mole
- Spindelevus
- Melonome
- Skin changes
Medical: nevus
English: mole, nevus, birthmark
Definition of birthmark
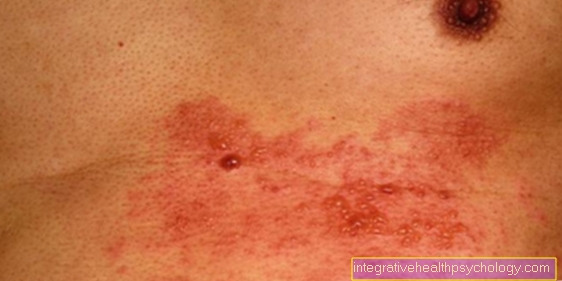
A nevus (birthmark) is a benign skin change. Usually this is well described.
This malformation of the skin can have different causes. With these nevi (plural of nevus) one can determine different origins.
Some of these spots are caused by certain skin cells called melanocytes. These produce the skin's dark pigment, melanin. (For example, the tan that occurs when the skin is exposed to the sun is based on the increased production of melanin.) This is also known as pigment nevi.
Other birthmarks come from single or multiple layers of the skin. These include, for example, epithelial nevi and connective tissue nevi (see below).
causes
Acquired moles develop in almost everyone. UV radiation / sunburn plays a major role in the development of liver spots. A suppressed immune system also seems to favor the development (increased occurrence with chemotherapy).
Nevi arise from the multiplication of nevus cells. It is suspected that these nevus cells are derived from the actual melanocytes.
Birthmarks, on the other hand, are usually congenital.
diagnosis

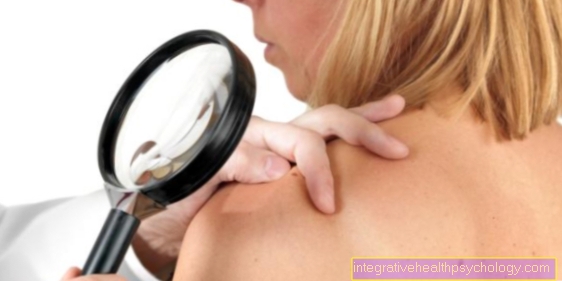
When making the diagnosis, it is particularly important to distinguish benign from malignant skin changes.
The dermatologist looks at the spots through a kind of large, illuminated magnifying glass. As a rule, a statement can be made as to whether the change is actually a benign or malicious change. If there is any doubt, a biopsy (sampling for tissue examination) can be performed. So some, or in most cases all of the dark area is removed.
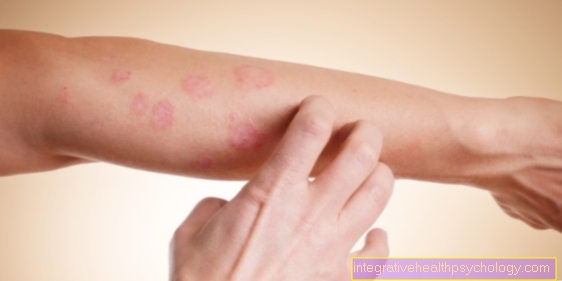
Birthmark itches
An itchy mole can be the first sign of a malignant skin lesion. In addition to the itching in the area of the birthmark, bleeding and the formation of scab-like deposits are also suspect.
Here, however, you have to pay attention to whether the bleeding comes directly from the birthmark or whether just scratching the itchy skin area has led to minor injuries. Patients who notice a mole that itches can use the so-called A-B-C-D-E rule to assess whether it is possibly a malignant melanoma at home.
If the birthmark in question
- asymmetrical shape
- fuzzy border
- the color changes
- has a diameter greater than 6mm or
- protrudes from the surrounding skin level
a doctor should be consulted as soon as possible. With a special microscope, a dermatologist can quickly assess whether the itchy mole needs to be removed.
Read more on the topic: Birthmark itches
A black birthmark that itches can indicate skin cancer and should be examined urgently. Read about it: Black birthmark - how dangerous is it?
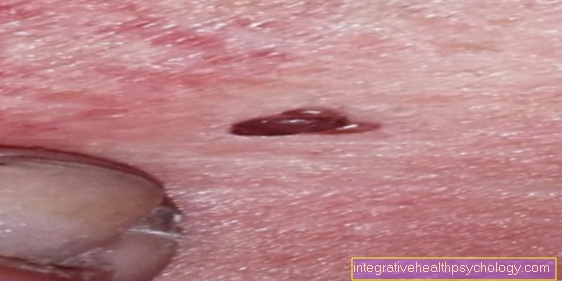
Birthmark hurts
A birthmark causes usually no pain. To step Pain or itching on, should according to the A-B-C-D-E rule (Asymmetry, limitation, colorization, diameter and development) a malignant degeneration to be clarified.
Besides the pain you can too Itching, bleeding, scaling, or tingle Be symptomatic and should be examined by the dermatologist.
It doesn't have to be a Melanoma exist, but the birthmark should definitely be closely controlled and the process can be documented.
course
Usually, birthmarks are benign and can be completely surgically removed if necessary. Once a mole is removed, it won't come back. However, it may well be a malignant tumor develop from it, which is why it must be carefully observed.
Remove / have the birthmark removed
Since the risks of surgical mole removal are relatively manageable, any noticeable skin changes are usually removed promptly. In an operation performed under local anesthesia, the whole birthmark is cut out of the skin. With this measure, care must be taken to ensure that a sufficient distance from the surrounding skin is maintained.
The necessary safety distance depends on the thickness and diameter of the suspicious mole. On average, approximately one to two inches of healthy skin is removed. Furthermore, the attending surgeon must ensure that all layers in the area of the affected skin area are completely separated apart from the muscle fascia. If the aim is to remove a conspicuous birthmark in the area of the face, the surgical intervention can be carried out with the help of a special microscope (microscopically controlled surgery).
In this way, the safety margin does not have to be widened too far, and the risk of unsightly scars developing is reduced. As malignant melanomas tend to metastasize into the bloodstream and / or the lymphatic system, a tissue biopsy is usually not taken.After the mole has been removed, the entire skin lesion is sent to a suitable laboratory and examined for malignant cell strains.
If a malignant melanoma is diagnosed after the mole has been removed, removal of the nearby lymph nodes may be necessary. Patients can also have a conspicuous birthmark removed using a special laser (see next section).
Typical complications that can occur if a patient has a suspicious birthmark removed are allergic reactions to the local anesthetic administered and / or other materials used (sutures, disinfectants, etc.). In addition, there is a possibility of excessive bleeding during or after the surgical treatment. For this reason, before performing the mole removal, it must be ensured that blood-thinning medication (e.g. ASA or Marcumar) is discontinued.
In some cases, after the mole is removed, infections occur along the wound area. Redness, swelling and the development of heat are the first indications of such a wound infection. With the help of a suitable antibiotic, such an infection can be quickly contained. In general, it can be said that complications are extremely rare when removing a mole. Fear of the side effects of the operation should not prevent a patient from having a potentially degenerate birthmark removed.
Depending on the thickness and diameter of the mole concerned, the prognosis varies after it has been removed. As a rule, small melanomas that have not persisted in the skin for long have a good chance of recovery. This fact is due to the fact that the metastasis tendency of a malignant melanoma is strictly dependent on the growth time. The faster a suspicious birthmark is removed, the lower the risk of metastasis and the better the chances of recovery. Metastases of malignant melanoma are in most cases im
- brain
- lung
- Skeleton or
- on other skin areas
to find. This fact makes it clear why an already metastatic birthmark has a poor prognosis even after the patient has had it removed.
Read more on the topic: Remove birthmark
Laser removal of a mole
A birthmark is one benign growth of the pigment-forming cells of the skin. Should it be from cosmetic or medicinal (Suspected malignancy) Reasons must be removed, offers itself in addition to the surgical also the Laser removal on.
To do this, the birthmark is advance chilled or possibly with a Local anesthetic stunned. Depending on Color, depth and size of the birthmark become different wavelengths used. The high-energy beam of the laser ensures that the target cell is heated up to the point of destruction.
The laser removal is imperfect and harbors that Risk of relapse. It can also happen that the birthmark only fades, but does not go away completely. However, since the suspicious tissue is badly burned by the heat of the laser, there is one Examination for malignancy of the tissue is no longer possible.
There are many different types of lasers. From the name of the treatment method it can usually be deduced which medium is generated to generate the rays, for example CO² laser, diode laser, ruby laser.
One usually occurs after treatment Reddening of the skin for a few days on, for deep and large treatment areas, a slightly pinkish, light spot stay behind. In the weeks before and after treatment you should Avoid sunbathing, solarium visits and cigarette smoking become.
Remove the birthmark yourself

Moles or moles are a nuisance to some people. Because of this, many patients come up with the most absurd ideas to remove the small spots. In the meantime, special creams are even offered, with which a birthmark can supposedly be removed by yourself. However, no actual medical efficacy can be proven for these products.
In addition, information is circulating about supposedly effective home remedies with which moles can be removed. Citric acid is said, for example, to effectively lighten dark skin changes and thus make them appear less noticeable. The application of apple cider vinegar to the affected areas of the skin should also serve to be able to remove a birthmark yourself. In addition, much more drastic measures are used in some patients. Many sufferers try to remove a birthmark themselves by cutting it out or tying it off.
Basically, from a medical point of view, it can be said that a patient should under no circumstances try to remove an annoying or conspicuous birthmark himself. Skin changes that appear suspicious must be examined by a dermatologist. Only this is able to assess whether the cells are malignantly changed and whether surgical removal is necessary.
The layperson is not able to conscientiously rule out the presence of a malignant melanoma despite some clues (for example the A-B-C-D-E rule). In addition, such skin changes should only be removed by a specialist under local anesthesia.
The anesthetic used also causes the smallest blood vessels to narrow and thus inhibits the flow of blood in the surgical area. Without proper anesthesia, cutting out a mole can be extremely painful and cause profuse bleeding.
In addition, the patient who removes a birthmark himself can provoke serious and sometimes life-threatening infections. Also the creation of a sepsis (Blood poisoning) is not uncommon in such independent experiments. Patients who want to get rid of an annoying birthmark should also note that if a malignant skin lesion is improperly removed, degenerated cells can enter the blood and / or lymphatic system. In this case, organ metastases are likely to develop. The fact that a suspicious mole must urgently be removed down to the muscle fascia contradicts the assumption that the patient himself can remove it completely.
Furthermore, the likelihood of unsightly scars developing is much higher if a patient decides to remove the birthmark himself. A final argument against cutting out skin lesions on your own is the fact that the formation of new moles was observed frequently.
Birthmark in the eye

A birthmark usually consists of melonocytes, i.e. cells containing melanin. Often the birthmark also comes from blood vessel cells, connective tissue cells or a number of other cells. Therefore, a birthmark can also develop in the eye, where all three of the cell types mentioned above are located.
The diagnosis of a mole in the eye usually comes as a surprise to the patient, as the fundus cannot be seen from the outside. A mole in the choroid (choroid), which surrounds the eyeball from behind, can only be diagnosed by an ophthalmologist. The birthmark can also remain undetected for years (as it is asymptomatic) and can only be determined during a routine examination.
If the ophthalmologist notices a change, such as sudden growth or deformation, the mole should be removed. This is done either through a minor eye surgery, laser removal, or radiation therapy. After that, a follow-up check at least every six months is advisable.
Frequent places of manifestation in the eye are the choroid, the eyelids, the iris and the conjunctiva.
The doctor also documents the findings and notes the position, size, shape, color and diameter in order to be able to assess the birthmark as it progresses.
For better representation, ultrasound or fluorescence angiography (representation of the blood vessels) is sometimes used.
Read more on the topic: Birthmark in the eye
prophylaxis
Since intensive UV radiation the degeneration of harmless birthmarks, you should avoid spending too long and often in the sun. Especially suffered in childhood Sunburns promote and increase the risk of developing one malignant melanoma.
Birthmarks should definitely be watched. Not only changes in color and structure, but also an itchy skin can be an indication of the origin of a Melanoma be. Fair-skinned people should be particularly careful about exposure to the sun. In addition, caution should be exercised if relatives have had different times.
Summary
The birthmark is the most common benign tumor skin. Birthmarks are already at the birth available.
Moles however, are acquired. Removal is rarely necessary.
Above all, the birthmark should be observed by the patient and the changes communicated to the doctor, as it is definitely a preliminary stage of one malignant melanoma (more vicious Skin cancer) can be. Due to frequent, severe sunburns, the risk increases later Skin cancer (e.g. melanoma).