Pain in the parotid gland
introduction
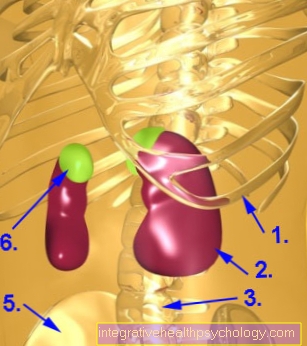
The parotid gland belongs to the salivary glands together with the salivary glands in the mouth and throat. It is also known as the parotid in technical terms. The saliva not only prepares food for digestion, but also ensures that the oral mucosa is kept moist. It also has an antibacterial effect.
The most common causes of pain in the parotid gland are inflammation or a salivary stone. In addition to the administration of painkillers for pain relief, attempts are usually made by massaging the parotid gland and chewing chewing gum to stimulate the flow of saliva to such an extent that the salivary stones dissolve by themselves.

causes
Parotid pain can have several causes. The most common cause is one Inflammation of the salivary glands. This is favored by poor oral hygiene and an unbalanced water-mineral balance. If little saliva is produced, this represents a considerable risk factor for the development of a salivary gland inflammation. As especially older people often only small amounts of liquid they are particularly at risk of developing an inflammation of the parotid glands. Another common reason for one to arise Inflammation of the parotid gland are Salivary stones, so-called sialolites. These can be found when the composition of the saliva is changed, for example in Metabolic disorders such as diabetes mellitus, can be the case or if people drink far too little.
Salivary stones can narrow the gland outlets of the parotid gland and thus impair the outflow of saliva. In this accumulated saliva can then Colonize bacteria and lead to inflammation of the parotid gland. They must be removed in any case in the event of complaints.
Also narrowed gland ducts, for example due to previous illnesses such as Cystic fibrosis or a mumps illness in childhood can be the trigger. Also certain Medicationwhich are taken for heart disease, allergies or depression can lead to decreased saliva production and consequent inflammation of the parotid glands. Alcohol can also promote this.
More information can be found here: Salivary stones of the parotid gland
Another cause of painful inflammation of the parotid gland is childhood illness mumps. However, this virus-induced disease has become very rare since vaccination was introduced.
Also can Tumors lead to pain in the parotid gland. These can be both benign and malignant, with the benign occur significantly more frequently.
Accompanying swelling
In addition to pain in the parotid gland, there is often swelling of the cheek. This is the case, for example, with inflammation of the parotid gland. A swollen parotid gland is typical for the childhood disease mumps, which is also an inflammation of the gland.
Pain and swelling are mostly unilateral. Other accompanying symptoms are hot and reddened skin in the area above the parotid gland and tenderness in the gland. With mumps, or in rare other cases, the symptoms occur on both sides. The pain usually increases when chewing, as more saliva is then produced. Since the parotid glands border on the temporomandibular joint and the jaw muscles, those affected can often barely open their mouth. In addition, inflammation leads to difficulty swallowing. Since it is an infection in the body, it usually reacts with a fever and swollen lymph nodes in the area of the gland.
You can read detailed information on this here: Swelling of the parotid gland
Pain without swelling
Parotid pain can occur without swelling. It can still be a Parotid gland inflammation act. The symptoms vary from person to person. But also small salivary stonesthat narrow the duct of the parotid gland can be the cause of pain without swelling. The pain often occurs at night, as the flow of saliva is then reduced. Parotid massages or sugar-free chewing gum or sweets help stimulate the flow of saliva and loosen the stones.
therapy
What can be done about the pain in the parotid gland depends on the cause.
This must therefore be clarified and especially with persistent pain or at Accompanying symptoms, such as. Fever, should be doctor to be visited. In order to be able to prove a salivary gland inflammation, a Blood test be made. If this is confirmed, as a rule anti-inflammatory drugs and Painkiller prescribed. If it is a bacterial infection, an antibiotic should also be taken. By a Ultrasound examination the doctor may be present Salivary stones or tumors detect.
In the presence of salivary stones you can special massages help the parotid gland to loosen the stones and move them outwards. Also can through sugar-free chewing gum or candy the flow of saliva can be stimulated and possibly trigger the salivary stones to come off. Drinking enough is also important. However, this only works with smaller stones; larger salivary stones can penetrate from the outside Shock waves be crushed. This is called extracorporeal shock wave therapy.
Also by one endoscopic intervention larger stones can be removed and narrowed gland ducts widened. If a salivary gland is constantly inflamed or if a tumor is found, it may be necessary to remove the parotid gland.
It is very important to treat inflammation of the parotid gland in good time, otherwise there is a risk of it Abscess and, in the worst case, blood poisoning. Above all, care should be taken to ensure sufficient therapy during each therapy Oral hygiene to be observed.
Home remedies for salivary gland pain
The most important thing to do with parotid pain is to maintain strict oral hygiene. This includes above all brushing your teeth regularly. Also one sufficient amount of water to drink is important to ensure a good flow of saliva. This is particularly important for the elderly, as they have a reduced need to drink. This can reduce the formation of salivary stones. In addition, chewing sugar-free chewing gum or sucking hard candy can help stimulate the flow of saliva and thus contribute to a reduced risk of salivary stones. Alternatively you can also gherkins which also stimulate the flow of saliva.