Pain in the lymph nodes in the groin
introduction
Lymph nodes are part of the immune system. They serve as local filter stations and are traversed by the body's lymph vessels. Foreign cells, such as B. Pathogens are via finely branched lymphatics from peripheral tissue z. B. skin or mucous membranes first passed on to local and then to central lymph nodes. If a pathogen gets into a lymph node, an immune reaction takes place there, i. H. Cells of the immune system become active and multiply in order, in the best case scenario, to destroy the pathogen - the lymph node swells and becomes visible as a small bump or can be felt under the skin.
You can find out more about the topic here: Swelling of the lymph nodes

Possible causes
Possible causes:
-
Abscess in the groin
-
Inflammation in the abdomen
-
viral infections (flu, glandular fever, measles, HIV)
-
bacterial infections (diphtheria, tuberculosis, borreliosis)
-
Cancer (malignant lymphoma, leukemia)
-
ingrown toenail
Here you can find out everything else about the topic: Causes of Lymph Node Swelling
Abscess in the groin
One of the most common causes of swollen and painful lymph nodes in the groin is local inflammation. Clogged sebum glands or ingrown hairs can lead to inflammation, which the body encapsulates in the form of an abscess.
Inside an abscess there are melted skin cells, pus, inflammatory and immune cells. Immune cells are formed in local lymph nodes, which meanwhile enlarge. If there is an acute process, the lymph node swells in a short time, which causes pain due to the expansion of the capsule and the surrounding tissue.
Pressure on the lymph nodes can make the pain worse. The knot is easily palpable and can be separated from the surrounding tissue. Other lymph node stations that are further away are usually not affected. The formation of an abscess suggests an intact immune system, as the body is able to isolate the focus of inflammation so that the inflammation does not initially spread. However, an abscess must always be surgically opened and rinsed. After that, the lymph node swelling quickly decreases.
Further information on the subject is available here: Abscess in the groin
Inflammation in the abdomen
Inflammation in the abdomen, especially in the small pelvis, can also cause swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin. Depending on which side the inflammation is on, the lymph nodes in the right or left groin may be more enlarged. Often one can find painful enlarged lymph nodes in the groin with appendicitis (appendicitis - especially on the right), ovarian inflammation (adnexitis - possible on both sides), or sigmoid diverticulitis (inflammation at the end of the large intestine - especially on the left).
However, inflammation in the abdominal cavity can spread quickly, activate lymph nodes on both sides and also cause general symptoms such as fever, shivering red and fatigue. In addition, several lymph nodes and several lymph node stations are usually enlarged and painful.
Ingrown toenail
Local inflammation in the area of the feet can also cause painful swollen lymph nodes in the groin on the same side. Ingrown toenails or athlete's foot cause bacteria to enter the body through the defective skin. The exogenous cells are directed into local lymph nodes via the lymph vessels.
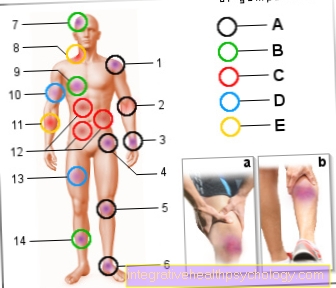
Such stations can be found everywhere in the body. Starting from the foot, pathogens first reach the small lymph nodes in the hollow of the knee, where some of the foreign cells can already be destroyed. The rest of them move on to the groin lymph nodes. There are numerous lymph nodes along the large vessels. Since there is usually little subcutaneous fat tissue in the groin area, the lymph nodes can be easily felt there.
Alternative causes for the pain instead of the lymph node
In addition to the lymph nodes, other structures in the groin can cause pain. A common cause of pain and swelling in the groin is an inguinal hernia. A weak point in the muscles or fascia creates a gap through which the bowel is pushed outwards. This shows up as a soft swelling in the groin. When pressing and standing, the swelling increases. If the intestinal part is pressed off by the break, severe acute pain can result. If the intestinal part is not moved back quickly, the intestinal tissue can die and cause severe infections.
Another reason for groin pain are strains or stretching of the groin muscles, such complaints are particularly common in competitive athletes. A worn (arthritic) hip joint can also cause pain in the groin.
Can that also be cancer?
Swollen lymph nodes in the groin can also be caused by tumor cells. Just like bacteria or viruses, tumor cells cause a local immune reaction in lymph nodes. In contrast to acute infections, this happens more slowly. The lymph nodes slowly increase in size, which is less or not painful. Tumors that cause swollen lymph nodes in the groin include: B. ovarian cancer, colon cancer, and testicular cancer.
More precisely, this is a tumor metastasis because the original cancer originated in another organ. In contrast, lymph gland cancer (lymphoma) starts directly from the lymph node. However, this usually affects several lymph nodes. For a precise diagnosis, suspicious lymph nodes are removed and examined histologically to find the primary tumor.
Unilateral pain
Unilateral groin pain can be found in the above-mentioned hernia, strain or stretching of the groin muscles also often occur on one side - especially on the dominant side, e.g. B. Ankle bone in long jump. With heavy load on both legs z. B. In martial arts both bars can be affected. Long periods of incorrect loading or misalignment can wear out the hip joint on the affected side and cause pain. Unilateral pain is caused by local inflammation, which can manifest itself as painful lymph node swellings in the affected side.
Bilateral pain
Bilateral groin pain is particularly common with generalized swelling of the lymph nodes. This can be found in viral or bacterial infections, especially in Pfeiffer's glandular fever a long-lasting painful swelling of the lymph nodes can be observed. But even with a simple flu, lymph nodes can swell all over the body; they are often best palpable in the groin regions and on the neck. Overloading through exercise can cause inflammation in both groins; the psoas and front thigh muscles are primarily responsible here. Pain can be triggered by pressure on nerves that run under the inguinal ligament (nervus cutaneus femoris lateralis) which radiate from the groin to the front and outside of the thighs. This is e.g. B. by wearing a too tight belt on one or both sides.
diagnosis
A good medical history and physical examination are crucial for a correct diagnosis. If one palpates the lymph nodes, one differentiates between enlarged, soft, easily movable, tender nodes, which indicates an infectious cause. Another distinction is made with enlarged, coarse, non-painful nodules that have grown together with the environment, which can indicate a tumor disease.
An acute course with bilateral lymph node swelling suggests an infectious cause. A blood count can confirm the suspicion of an infection. More accurate blood tests to identify bacteria or viruses may need to be performed. If the cause is in the abdomen, an ultrasound or MRI can provide further information. If a tumor is suspected, a suspicious lymph node can be removed and examined histologically.
You can find out more about the topic here: Inflammation of the Lymph Accounts - How Dangerous Is It?
Other accompanying symptoms
The swelling of a lymph node is a sign of an activated immune system and this can cause general symptoms such as fever, chills, fatigue or tiredness. Such symptoms are mainly found in viral or bacterial infections.
Local infections like abscesses or ingrown toenails cause local reactions like overheating, redness and pain in the affected area. General symptoms are rather rare here or only appear in severe cases.
If the cause is in the abdomen, abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, nausea or tenderness may occur.
Gynecological reasons can lead to increased or irregular menstrual periods.
Cancer also causes so-called B symptoms, such as fever, night sweats (very profuse sweating at night) and unwanted weight loss (10% of body weight in 6 months).
Treatment and therapy
Therapy depends on the cause. In the case of local causes such as an abscess or ingrown toenails, the defect must be surgically removed. If the inflammation has spread further, an antibiotic may have to be taken for several days. Inflammations in the abdomen such as appendicitis must also be surgically treated promptly.
If it is a minor infection, such as the flu, the best therapy is physical rest and sufficient fluid intake. In addition, painkillers and antipyretic drugs can be taken.
If cancer has been diagnosed, a stage-appropriate therapy with surgery, chemotherapy and / or radiotherapy must be initiated after a precise staging.
Duration and forecast
The cause is also decisive for the duration and prognosis. Local inflammations or simple infections usually heal without consequences after a few weeks with appropriate therapy. More serious infections such as Pfeiffer's gland fever can take a long time and cause the person affected to have recurring attacks.
In the case of HIV infection, new drugs lower the viral load below the detection limit and slow the course of the disease, but the disease is not curable. Some cancers are also partially treatable. If lymph nodes are already infected, it is a higher stage and life expectancy is significantly reduced compared to healthy ones.
Find out more about the following topic: Duration of lymph node swelling
Recommendations from the editorial team
You can find more information about lymph accounts in the following articles:
- Causes of Lymph Node Swelling
- Chronic swelling of the lymph nodes
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes


.jpg)