transplantation
definition
The transplantation of organic material is called transplantation. These can be organs, but also other cells or tissues, such as skin, or entire body parts. The transplant can either come from the patient himself or from another person. A distinction is made between living donation and post-mortem organ donation, with living donations only allowed from close relatives.
A transplant is necessary if the organ in question is irretrievably inoperable. For patients to whom this applies, a transplant is often the only chance to survive.
There is clearly more need for donor organs than available organs, therefore it must be clearly regulated how the donor organs are distributed. In Germany this is supported by the Transplant Act regulated. In order to receive a donor organ, the patient must be placed on a waiting list by the doctor treating them. Depending on the urgency and the prospect of success, the ranks and thus the donor organs are assigned. There are several organizations in Europe that mediate post-mortem donor organs across Europe.
There is one in Germany Organ donation card. This gives you the opportunity to decide before your death whether you want to act as a donor or refuse an organ removal.
After a successfully performed organ transplant, the patient must regularly take certain medications, so-called Immunosuppressants, through the one Rejection reaction is suppressed.
What is to be considered?
After the transplant is it required that regular follow-up appointments be respected. These serve to identify possible late effects or reactions and to do something about it. Immediately after the operation, it is important that the doctor tells the patient how they should behave with the transplant in everyday life and which ones Medication need to take them regularly. This includes above all immunosuppressive drugsthat ensure that the transplant remains functional and is not rejected by the body's own defense reaction. By regular checks the medication can be optimally adjusted.
Through this immunosuppressive therapy, the suppresses the body's defense against infections. This is why transplant recipients are special susceptible to bacterial and viral diseases. Immediately after the operation, it is important to ensure that the freshly operated on are protected from germs as well as possible. A mouthguard to prevent the transmission of bacteria through droplet infection is useful. If signs of an infection appear, a doctor should be consulted immediately, as these can be very serious for the patient.
Immunosuppressants
A medical therapy with immunosuppressants is after every transplant required. These drugs suppress the body's defense system. The immune system is responsible for recognizing foreign bodies and taking active action against them. In the case of bacteria or viruses, this is also sensible and useful. However, the transplanted organ is also a foreign body and is treated like one by the immune system. Without further action, the donor organ would be destroyed become. In order to prevent this, however, the immune system inhibits the body's own defense system and is not directed against the transplanted organ.
The disadvantage is that the immune system then changes also no longer against other foreign bodieshow bacteria aligns. Thus, these are the patients who are taking immunosuppressive drugs very susceptible to bacterial and viral infections, as well as for fungal diseases. You should protect yourself against any germs, especially immediately after the procedure.
There are several drugs that are used for immunosuppression. They are dosed at their highest in the period immediately after the organ transplant, as the risk of transplant rejection is then highest.
Risks
Depending on the size and length of the surgical procedure, there is a risk that during and after the operation Bleeding occur. Often the surgeons have to cut large blood vessels during an organ transplant and sew them up to the new organ. In addition, the risk is a infection elevated.
After the transplant, the greatest risk is one Organ rejection by the body's own defense system. This occurs when the immune cells recognize the transplanted organ as a foreign body and destroy it. Because of this, a immunosuppressive therapy is very importantto weaken the immune system. Such rejection can occur right after surgery, a few weeks later, or even years after the transplant.
With a living donation, there is also the risk that a healthy person will be exposed to a risk situation, namely the operation, and complications may arise during or after the procedure.
Types of transplants
Kidney transplant
At a Kidney transplant a donor kidney is implanted in a patient with kidney disease. This is necessary when both kidneys of the sick person fail. This can be the case due to various diseases. Which includes Diabetes mellitus, Glomerulonephritis, Shrunken or cyst kidneys, severe tissue damage from urinary retention, or nephrosclerosis, in which the kidneys are damaged by high blood pressure.
At Kidney failure the patient can first contact the dialysis connected. This is a machine that does the kidney function. Regular connection to dialysis, however, brings considerable restrictions in everyday life, which is why a kidney transplant is often the only promising option.
A kidney transplant can be both Living donation as well as post-mortem donation be performed. Since the healthy person has two functioning kidneys, he can donate either of the two without being restricted himself. A kidney as a living transplant proved to be much more durable and functional than transplants from the deceased. Most transplants, however, come from the deceased. On average, after about 15 years, the transplanted kidney begins to lose function and a new transplant is required.
After the operation, the laid Urinary catheter about 5 to 6 days to drain the urine so the sutures on the bladder can heal. If the transplanted kidney does not work immediately and produces urine, dialysis therapy may be necessary for a few days.
Liver transplant
A Liver transplant is in patients with chronic or acute Liver failure necessary. The most common reason why patients are put on the waiting list for a donor liver is alcoholic cirrhosis. But also through medication or hepatitis can a Cirrhosis of the liver triggered and a transplant is necessary. Other reasons for a liver transplant are Tumors, vascular diseases or congenital metabolic diseases how Hemochromatosis or others.
Most of the donor organs come from the deceased. However, it is also possible that only one Part of the liver transplanted which is taken from a living donor. These partial liver donations can be found mainly with parentswho have this donate to your child. It is also possible with a post-mortem donor liver the Organ to share. The larger part is then planted in an adult, the smaller in a child. This procedure is called Split liver. The 10-year survival rate of a patient who received a donor liver is around 70%.
Lung transplant
To get to the Waiting list To be set for a donor lung is a must ultimate lung failure present, which requires lifelong respiratory insufficiency treatment. In most cases it is chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseleading to such organ failure. But also other diseases like Cystic fibrosis, Pulmonary fibrosis, an inflammation of the alveoli (Alveolitis), Sarcoid or high blood pressure in the pulmonary circulation (pulmonary hypertension) could be reasons for a lung transplant. A lung transplant can be either carried out on one or both sides become. In some cases, the function of the heart is impaired in addition to the lungs. Then a combined heart-lung transplant is necessary.
Because only very few donor lungs are available, the criteria according to which they are awarded are accordingly strict. The patients must not have any other serious illnesses and must be younger than 60 years for a unilateral transplant, younger than 50 years for a bilateral transplant to be eligible as recipients. In addition, life expectancy must be less than 18 months.
The Life expectancy after a successfully transplanted lung lies by about 5 to 6 years after the operation. The first two to three weeks after the procedure are very critical and it often happens Rejection reactions.
Heart transplant
A Heart transplant comes into question if the patient's heart is severely impaired in its functionality and can no longer be improved through therapeutic measures. The majority of heart transplants are in patients with a Heart failure (Heart failure), which is due to inflammation of the heart muscle (Cardiomyopathy). In rare cases you can also Valvular heart disease or congenital heart defects require a heart transplant.
Only those deceased who have not suffered from a pre-existing heart disease are admitted as donors. In addition, the The size of the donor and recipient heart match. Since the waiting time is often very long until a suitable donor heart is found, you can to bypass heart pumps which support the pumping function of the heart muscle.
In some cases, in addition to the patient's heart, the lungs are also irreversibly damaged. Then one must combined heart-lung transplant be performed.
Often it happens to Rejection reactions after the operation. In the first year after the operation, an average of every 10th patient dies with a donor heart.
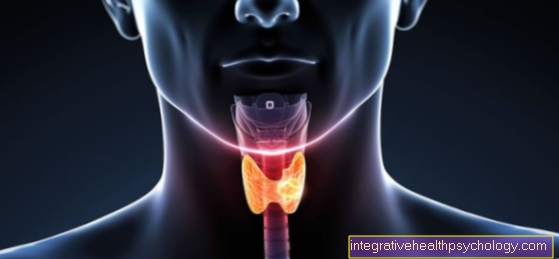
Pancreatic transplant
To be approved for a pancreatic transplant, the patient must contact Type I diabetes Suffer. The pancreas must no longer produce insulin and the patient must requires dialysis be on the waiting list for a pancreatic donation.
Often due to type I diabetes Vascular damage occur that primarily damage the kidneys, complete kidney failure may result in a combined pancreatic kidney transplant is required.






.jpg)