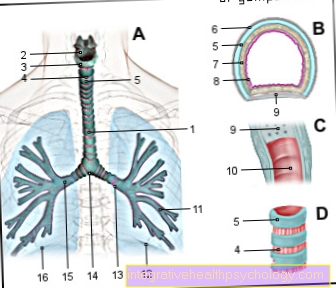
Canine tooth in the baby
The child's deciduous dentition consists of 20 teeth, five per half of the jaw in the lower and upper jaw, including two molars, two incisors and a canine tooth in between. The four canines owe their name to their position in the dental arch from its clear kink in the jaw. The canine tooth is conical and tapering to a point and is pronounced in all mammals. In humans, however, it is only remotely reminiscent of the strong fangs and tusks of predators, but due to its particularly long root (the longest of all roots in the entire set of teeth) it is very robust and firmly anchored in the jaw and is therefore used to hold on and bite off Food.

Eye tooth
The term “eye tooth” is a rather outdated term for the human canine tooth in the upper jaw. Nevertheless, it still has a meaning today, because due to its position in the jawbone and its particularly long root, its tip can reach the bony eye socket and the lower eye nerve (Infraorbital nerve) pass. If the upper canine is inflamed, it can then spread to the face and be accompanied by swelling, pain and a feeling of pressure, especially in the region of the eye, both in adults and in children and babies, which makes it the most unpopular tooth with parents.
You can find more information about the canine here: canine
When do babies teething?
The baby teeth in the jawbone of the baby break through in a certain order, what is called "first dentition". This usually begins between the ages of six and ten months. Then you can recognize the beginning of the tooth eruption by the unevenness in the gums. The four canines in the deciduous dentition usually appear in the 16th to 20th month after birth.
Also read: Teething of the molar in the baby
What to do if the canines don't come
There are several reasons why the deciduous canines do not erupt.
- On the one hand, it may be that the tooth germ has been damaged by trauma and the tooth does not come out.
- It is also possible that the teeth have an obstacle to penetration and remain in the jawbone. This is the case, for example, if the other teeth erupt in the wrong position or if there are so-called double systems. This means that there are, for example, more than 4 incisors and the canine then has no space to break through.
- In some diseases, such as Down syndrome or in children with a cleft lip and palate, the deciduous canines may be missing.
However, aplasia, i.e. failure of teeth, occurs more frequently in permanent teeth and only very rarely in milk teeth. In the permanent teeth, the canine is only affected in 9% of cases. However, if the milk tooth is not already in place, this can often be a sign that the permanent tooth will not erupt either.
In the case of milk teeth, it is important to know that they have a so-called placeholder function. If the canine teeth are lost prematurely, or if they do not even break through for the reasons mentioned, there may be deviations in the position of the permanent teeth.
Bite anomalies, language problems, temporomandibular joint problems or aesthetic impairments can also be possible.
An X-ray image, which can be made if one expects the eruption of the permanent canine (in the upper jaw at around 11 years of age, in the lower jaw at 9 years of age), provides certainty as to whether a permanent canine is in place.
When do I have to go to the dentist?
If you notice that your baby's canine is not coming out at all or is erupting in the wrong position, it doesn't hurt to go to the dentist early. However, in most cases there is no need to worry about a delayed eruption of milk teeth. However, if the permanent tooth is also not in place, you can discuss later treatment options with the dentist at an early stage. Early clarification can be very helpful here.
When is a crooked canine problematic?
As a rule, you do not have to worry about crooked teeth in the deciduous dentition. A crooked tooth is more likely to be observed in permanent teeth. The canine is particularly often affected here. One often speaks of the so-called "canine tooth outward standing", which should be corrected orthodontically.
A crooked canine can have various causes in the deciduous dentition.
- Genetic influences and growth processes play a major role here.
- However, certain habits, such as thumb sucking or sucking, must also be observed here.
In particular, prolonged use of pacifiers or prolonged use of bottle feeding can lead to misaligned teeth, which can often affect jaw growth and lead to permanent damage. Weaning off pacifiers early is particularly important here.
How long does it take for the teeth to erupt?
Basically, the duration of a tooth's eruption varies greatly from child to child, but also from tooth to tooth. Some teeth come quickly, only need a few weeks, other teeth prove to be very stubborn and can then take up to several months to fully erupt.
Painful teething
In general, this is a natural process that occurs without major problems for many children, but pain is not uncommon. Especially at the beginning, the pressure in the jaw increases, because the teeth push to the surface as their roots grow. In addition, the gums are particularly irritated as they get thinner and thinner and eventually tear. It can appear very red and swollen. Most of the time, the sharp canines hurt more than other teeth.
In any case, it helps to let the child chew on special teething rings made of full silicone. These promote tooth eruption and relieve pain. Cooling measures such as putting on damp washcloths and pieces of fennel or carrot are also helpful. If placed in the refrigerator beforehand, these produce a decongestant and pain-relieving effect. (Caution: Do not put it in the freezer! The gums may freeze.) A simple finger massage can also help by rubbing the gums with cold chamomile or fennel tea.
Another possibility is so-called teething gels, which contain a local anesthetic and thus ensure rapid, short-term pain relief. In some cases, paracetamol suppositories are also recommended. However, this should be discussed with the pediatrician beforehand.
Sometimes it is advised to let the baby bite on the amber necklaces worn around the neck. These are supposed to relieve your child's pain through essential oils and vibrations. But there is danger to life here! The baby can become strangled or choke on small, loosened beads. That's why pediatricians advise: hands off!
In general, however, it helps the child the most if they are given good advice, they are comforted and a lot of distraction so that they can get through the time of the eruption quickly.
More information can be found here: Teething in the baby
Concomitant symptoms
In addition to the typical dental fever, other symptoms can also occur during teething. The processes in the oral cavity mainly stimulate saliva production and the baby drools more than normal. It also has a strong need to chew on objects or on its own fist in order to facilitate the penetration of the teeth. Special teething rings that protect the hand from injury help here. In addition, the gums are noticeably reddened, swollen and very sensitive at the breakout points.
It is also noticeable that the children have little or no appetite, but have a very good digestion, which is why diarrhea can occur, which can consequently lead to a sore bottom. Creams and powders can help.
Read more on the subject at: Diarrhea while teething
All of this leads to the fact that the babies sleep very restlessly or not at all, especially at night, are very cranky and scream and cry more often. If this condition lasts longer and if fever and diarrhea occur, it is always advisable to consult a doctor.
You can find more information at: Fever when teething and Teething in the baby