Ringing in the ears
Synonyms
tinnitus
engl. tinnitus
introduction
Whistling in the ear is not dangerous, but it is extremely stressful for many people. Find out everything you need to know about tinnitus here.

Are noises in the ears auditory perceptionswhich can be traced back to various causes and malfunctions. The type and intensity of the noise in the ear can vary. You can do both one-sided as well as both sides occur. Although tinnitus is more of a symptom, according to the ICD-10 it is managed as an independent diagnosis.
Noise in the ear is classified based on various criteria. A distinction is made between a subjective and an objective tinnitus as well as an acute (duration less than 3 months) and a chronic tinnitus (duration over 3 months). Furthermore is also the Place of origin the noise in the ear is important. The tinnitus can be outer ear, Middle ear, Inner ear but also in the Audio track or in brain arise. Ultimately, the tinnitus will still be in Degrees of severity divided, which relate to the quality of life in the private as well as in the professional area. Grade 1 does not correspond to any psychological stress, grade 4 leads to occupational disability and is associated with a very high psychological stress. The type of ringing in your ears can be very different.
frequency
According to their own statements, around 25% of the German population have already experienced tinnitus, 4% even suffer from chronic, i.e. persistent, tinnitus. The incidence, i.e. the number of new cases in the population, continues to rise. Presumably, increased noise exposure has something to do with it. The tinnitus manifests itself mostly between the ages of 40 and 50. Men and women are equally affected.
causes
There are many causes that can lead to tinnitus. A distinction is made between those that lead to an objective finding and those that cause a subjective noise in the ear.
Also read more on the topic: Tinnitus cause and these symptoms can be used to recognize a magnesium deficiency
Objective noise in the ear
A stenosis (narrowing) of the carotid artery, for example, can lead to an objective noise in the ear. Typically, there is then a pulse-synchronous noise. Other flow noises from vessels (arteries) are also possible.
Please also read our article on this Clogged carotid artery (carotid stenosis)
Another cause is a tumor of the Glomus tympanicum. This is a tumor of the middle ear caused by a cluster of nerve cells called the Paraganglion tympanicum, goes out. The tumor also causes a pulsating noise in the ear (usually a hissing noise), which can be associated with hearing loss.
Furthermore, breathing sounds, vascular malformations (aneurysm, AV fistula), tension in the middle ear muscles or opening movements of the ear trumpet can cause objective tinnitus.
In the case of such objective noises in the ear, the treatment of the underlying disease is at the fore of the therapy. However, this is not always possible.
Subjective noise in the ear
The subjective tinnitus is only perceived by the person affected. The causes can be divided into four categories:
- Intra- and extracranial causes
These causes can be both inside the skull and outside. This group includes tumors (e.g. Brain tumors, Acoustic neuroma), Trauma (traumatic brain injury, Petrous bone fracture) and operations (e.g. on the brain or ear).
- Mental causes
stress and big mental stress can lead to tinnitus. However, they can also accompany tinnitus or be the result of chronic noises in the ear. The more distressing the noise in the ear is for a person, the more likely it is that accompanying psychological symptoms, for example a depression, occur.
- Systemic diseases
These include, for example cardiovascular diseases such as high blood pressure or irregular heartbeat. Furthermore, a Hyperthyroidism, multiple sclerosis or that Cervical spine syndrome be a cause. Also psychiatric illness such as schizophrenia can cause auditory hallucinations. Strictly speaking, however, this is not a typical noise in the ear.
- Functional disorders of the ear and the central auditory pathway
Damage to the ear and the central auditory pathway can lead to the perception of annoying noises in the ear, sometimes painful hyperacusis or even hearing loss. Triggers are for example inner ear toxic drugs (Drugs that damage the ear) like Loop diuretics or Aminoglycosides (Gentamycin, erythromycin). The latter can be acute or chronic Acoustic trauma cause. Also inflammation in the ear, like Otitis media or Labyrinthids, can lead to a ring in the ear. Other diseases such as otosclerosis, the Meniere's disease, the Eardrum perforation as well as the Sudden hearing loss are also to be mentioned. The latter is accompanied by sudden inner ear hearing loss and a feeling of "cotton wool in the ear", which is often accompanied by tinnitus.
Ringing in the ears with a cervical spine syndrome
The symptom complexes in a cervical spine syndrome can be very different. Often there are ringing in the ears, dizziness, sore throat and neck, and tingling / numbness. Functional, degenerative or traumatic processes can be considered as causes. Possible causes are for example a Whiplash, functional tension or a Facet syndrome.
The muscular tone of the cervical spine influences the function of the cranial nerve nuclei, which are essential for the function of hearing. Disturbances in auditory perception can be attributed to tension or joint problems in the cervical spine. Furthermore, the blood circulation also plays a role Cranial nerve nuclei an important role. These are sometimes supplied by vessels that run close to the cervical spine.
Degenerative changes in the bony structures of the cervical spine can narrow these vessels and thus impair the blood flow to the cranial nerve nuclei. The type of ringing in your ears can vary. But often it is from one deep, muffled, one-sided tone reported or from one irregular noise.
Also read more on the topic: Cervical spine syndrome tinnitus
Symptoms

Affected people describe the noises in their ears as hissing, humming, whistling, cracking or knocking. The noise can also have a rhythmic, pulsating character or be more monotonous. In addition, it can become a Hearing loss, but often even to one Hyperacusis come. Those affected often have comorbidities (accompanying illnesses) such as Muscle tension in the jaw and in the cervical spine, depressions, Anxiety up to Suicidal ideation on. Sleep disorders due to the unpleasant noises in the ears are also common. a headache and dizziness as well as a Hearing impairment are often described.
Also read more on the topic: Tinnitus symptoms
Noises in the ears while lying down
Some people take their noises in their ears stronger when lying down true or claim to hear a louder noise than usual, especially in the morning after getting up. This may be due to the fact that a greater silence prevails than at the rest of the day. The same applies to waking up in the morning. Accordingly, the body is not distracted by other stimuli and there are no other noises that could superimpose the annoying noise in the ear.
It can help soft relaxing music when falling asleep to listen. Also can Relaxation techniques help you not to fixate yourself so much on the noise in your ear and thus perceive it as less annoying.
therapy
Therapy for tinnitus includes various approaches, some of which aim at a cure, others are only intended to improve the quality of life and the symptoms. To prevent a chronic course, it is important to start therapy as early as possible. This is the best way to get a cure.
Also read more on the topic: Tinnitus treatment
Therapy of a ringing in the ear in the acute situation
In the acute situation, the tinnitus is usually treated with measures to promote blood circulation, Corticosteroids and one ionotropic therapy (Influencing the ion channels in the inner ear). However, the procedures are controversial as to their usefulness.
Therapy for an objective ring in the ear
In the case of an objective noise in the ear, the therapy is initially based on the Underlying disease. This can be, for example, the removal of a tumor or the neuroradiological, microsurgical or radiotherapeutic ablation of the body's own sound source.
Therapy for a subjective noise in the ear
In the case of a subjective ringing in the ear, therapy includes both causal and supportive measures.
- Causal therapy
This is only possible if the cause of the ringing in the ear is known, then therapies can be initiated that are intended to remedy the underlying cause. These include a antihypertensive therapy with high blood pressure, operational procedures for middle ear damage or physiotherapy in cervical spine syndrome.
- Supportive therapy
The supportive therapy measures are used when the cause of the ringing in the ear not known exactly or the cause cannot be treated causally. These are the building blocks of supportive therapy Tinnitus counseling, in which coping strategies are discussed, relaxation procedures and hearing therapy measures. In addition, a Habituation therapy take place, in which the affected person should be desensitized to the annoying noise in the ear.
A recommendation for drug therapy, for example with Ginkgo biloba or Glutamate antagonists, cannot be expressed according to the current state of research. Overall, recommendations are made for a few of the therapeutic measures that are frequently used. At the moment, evidence-based therapy for chronic tinnitus consists of tinnitus counseling, followed by cognitive behavioral therapy, in which patients should learn to deal better with the noise in the ear. It is also recommended to treat concomitant illnesses such as depression.
Other therapeutic approaches, the benefits of which have not been confirmed, include the acupuncture and Music therapy.
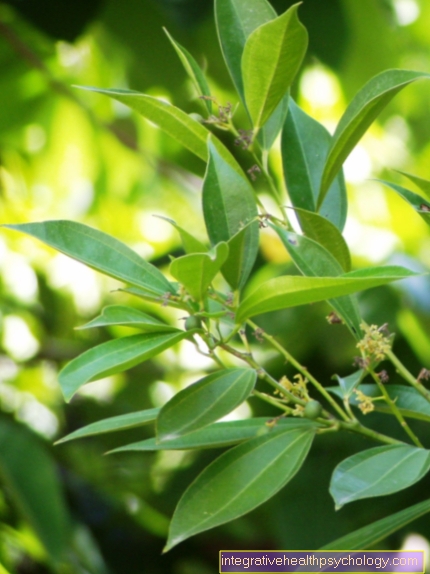
Tebonin®
Tebonin® is the trade name for a preparation with the active ingredient Ginkgo Biloba EGb 761. This is a Dry extract from the leaves of the ginkgo. It is approved in Germany for the symptomatic treatment of memory disorders, ringing in the ears, dizziness, circulatory disorders, concentration disorders, dementia and headaches.
Tebonin® works via two main mechanisms, one of which comes into play primarily in the acute phase of tinnitus, the other in the chronic phase.
- Acute phase
In the acute phase will the blood flow to the inner ear promoted, whereby ear noises can recede.
- Chronic phase
In the chronic phase the Ginkgo extract especially through his neuroprotective factors against the noises in the ears. He's supposed to Networking of nerve cells and signal processing in the brain promote. This can possibly be attributed to the fact that active ingredients of ginkgo affect gene expression and signal transduction. This should improve the perception of the noises in the ear in the chronic stage and make it easier to get used to the noise. The manufacturer makes the daily intake of 120 mg ginkgo special extract EGb 761® for at least 12 weeks recommended. It should be noted, however, that a large number of patients report side effects such as dizziness, nosebleeds, and an increase in ringing in the ears. The intake should therefore be discussed with a doctor. In the current medical guidelines, its use is not recommended.
Ringing in the ears during pregnancy
Many women report ringing in their ears pregnancywhich often disappear after birth. However, it is not possible to narrow down the exact percentage of women who experience ringing in their ears during pregnancy.
In principle, the same causes that otherwise cause noises in the ears can lead to noises in the ears during pregnancy. Also an increased stress level, Incorrect loads or one lack of mobility of the cervical spine can cause ringing in the ears of pregnant women.
It is advisable to see a doctor as early as possible so that therapy can be initiated. Then the chances are the best that the noise in the ear will not become chronic.
Ringing in the ears in children

The study situation on children's ear noises is not unambiguous, but it appears that around 15-20% of schoolchildren stated that they had already perceived an ear noise. There can be different reasons.
Children are more common than adults of Otitis media which can cause the ringing in the ears. Also congenital hearing loss or one Noise pollution can be causes of noises in the ears of children. Also play psychological factors, how stress or charges, an important role in the genesis of noises in the ears in children.
However, unlike adults, children are usually better able to block out the noises in their ears or to perceive them as not stressful. Therapy should therefore be based on whether and to what extent the tinnitus burdens or affects the affected child. Therapy is essentially analogous to therapy for adults. Treatment with medication should, however, be cautious at first. Much more important is hearing training or the treatment of underlying diseases.





.jpg)